
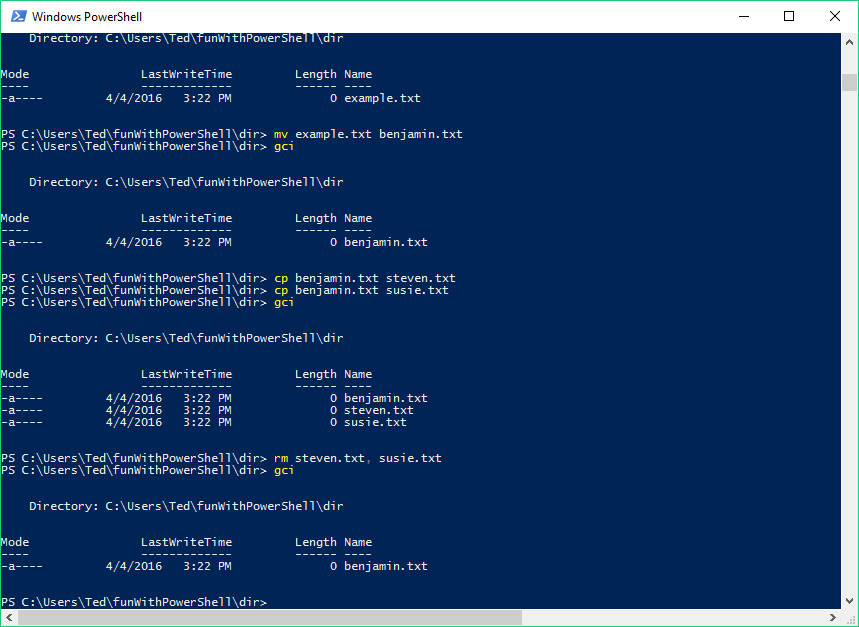
The final set of three rwx or - characters indicate everyone else’s permissions. The middle set of three rwx or - characters indicate the group’s permissions. The next three characters indicate the owner’s permissions: - for no access, r for read access, w for write access, and x for file execute access or folder browsing access. The first character is item type: - for file, d for folder, and l for symbolic link. The syntax for the abbreviated information section is: Information appears from left to right: the number of hard links associated with the item (for most users, this particularīit will be trivial information), the assigned owner, the assigned group, the last modification date, and finally the item’s The first string of characters at the beginning of each line is shorthand for the item type and permissions. The most basic ls option for viewing file and folder ownership and permissions is –l:ĭrwx-+ 5 michelle staff 170 Aug 20 15:49 Desktopĭrwx-+ 3 michelle staff 102 Aug 20 01:08 Documentsĭrwx-+ 3 michelle staff 102 Aug 20 01:08 Downloadsĭrwx- 19 michelle staff 646 Aug 20 01:08 Libraryĭrwx-+ 3 michelle staff 102 Aug 20 01:08 Moviesĭrwx-+ 3 michelle staff 102 Aug 20 01:08 Musicĭrwx-+ 4 michelle staff 136 Aug 20 01:08 Picturesĭrwxr-xr-x+ 7 michelle staff 238 Aug 20 15:29 Publicĭrwxr-xr-x 5 michelle staff 170 Aug 20 01:08 Sites Here, you will be presented with a few fundamental permissions viewing options. You can learn more about all the options available The ls command has many options for viewing nearly any file or folder attribute. Once again, the ls command is your primary tool for viewing file and folder information in the command line. The command line concepts in Chapter 3, “Command Line and Automation,” before reading the remainder of the section. For example, the pathname My Disk is “My Disk” or My\ Disk.If you aren’t already comfortable with navigation in the UNIX command line, then it’s strongly recommended that you study Although some file systems permit the use of these other characters, including spaces, you might need to add single or double quotation marks around pathnames that contain them.įor individual characters, you can also use an escape character-that is, put a backslash character immediately before the character in your string. 
Avoid most other characters, including space characters. Most of these users aren’t traditional user accounts with home directories, but you should be able to find the short name of known users on the computer.įile and folder names can include letters, numbers, a period, or the underscore character. In macOS, this folder is in the local /Users folder or on a network server.įor a list of short names on your server, enter dscl. To specify another user’s Document folder, use the short name preceded by the tilde (~) character-for example, ~jsmith/Documents.
For example, to specify the Documents folder of the current user, enter ~/Documents. The tilde character represents the home folder of the logged-in user. For example, the string “./Test” represents a sibling folder (named Test) of the current folder. Two periods represent the parent folder of the current folder.
For example, the string “./Test.c” represents the Test.c file in the current folder. A single period represents the current folder.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
